
Introduction
It’s like the old saying: you wait for ages for a bus, then two come along at once. In the last year we have seen Rycote (well-established in terms of shock mounts and windshields, but fairly new to making mics themselves) announce a small figure-of-eight mic in the form of the BD-10 (which I have tested previously), to form one of a family of seven mics; and Sennheiser soon followed with its announcement of the MKH 8030. The Rycote mic is starting to ship about the time I write this, and the Sennheiser mic is due to become available to buy in the second quarter of 2024. Of course, new mics are being announced all the time, but what is interesting about both these mics is the polar pattern and size: there are relatively few figure-of-eight SDC mics, with many well-known mic manufacturers having no such offering (for example DPA, Rode and, since the demise of the Blueline range, AKG). While the BD-10’s selling point lies in it being an excellent sounding fig 8 in the largely unpopulated mid-price range (albeit arguably boxing above its weight), the interest in the Sennheiser MKH 8030 is rather different: it is a member of the successful Sennheiser MKH 8000 family of mics, which have already established themselves as first-rate and robust workhorses of sound recordists across a range of disciplines including production sound, effects recording, nature recording and music recording. The company launched the first three of the series back in 2007 and the promised fig 8 model has been highly anticipated since, albeit with hope fading somewhat to resignation that it would never appear: there had been no additions to MKH 8000 series since 2012 until this new mic . Indeed, the first photos of the MKH 8030 in the wild last autumn led some to cry out ‘fake’! Fortunately, such cynicism (or, more charitably, self-protection against false hope) was ill-founded and the mic is a reality.
And why does the arrival of the MKH 8030 matter? Well, first off, it makes the MKH 8000 series mics a pretty complete family at last, with polar patterns comprising omni (MKH 8020), wide-cardioid (MKH 8090), cardioid (MKH 8040), super-cardioid (MKH 8050), short shotgun (MKH 8060), long shotgun (MKH 8070) and, now, fig 8. Given a straight choice many would rather use one range of mics for consistent sound, and this is especially significant when dealing with fig 8 mics, so often used for mid-side and double mid-side in combination with other polar patterns. Second, it means Sennheiser provides users wanting a fig 8 all the advantages of the rest of the MKH 8000 range – small, modular mics with extended high and low frequency response and with the legendary humidity resistance of all Sennheiser’s MKH mics: the latter being common to their radio-frequency (RF) design. It isn’t going to take over from the larger MKH 30 mic (launched back in 1987) for many users, any more than users of the MKH 40 cardioid mic automatically swapped to the MKH 8040, but for those wanting a smaller mic without giving up low self-noise (the new mic matches the 13dBA of the MKH 30), then this will be so welcome. Small size, of course, is as relevant to using mics on the end of a boom pole as it is for discreet micing in the concert hall, church or theatre, and as it is for creating complex (double mid-side and beyond) arrays in windshields for field recording. And, finally, with the MKH 8030 offering the advantages of the MKH 30 – not least RF design and low self-noise – it has a significant edge over the few alternative small SDC fig 8 mics currently available.
A word about these tests
Oh, a quick word about the tests below, less you expect too much and then feel disappointed, or, worse, chastise me! There is no substitute for putting a mic through its paces yourself, and nothing I can do will do that for you. Those from classical recording engineers with more refined ears and years of experience of working in the best concert halls, to production sound recordists working with the pressures of a major movie set, to wildlife recordists out there in extreme conditions that most us couldn’t handle even without a microphone in hand will need to see if the mic works for them and, critically, how it compares to whatever they have been using hitherto: that might be a Schoeps MK8 + CMC or the smaller CCM8, Sennheiser’s own MKH 30, or another fig 8 mic. I can’t replicate these different uses, and I don’t have every fig 8 mic on the market. So what follows will be, as ever, a series of recording tests relevant to my uses, a consideration of the mic on its own merits and, where useful, comparing the MKH 8030 to other mics I have here: this includes two other fig 8s that readers of this blog will know that I have used extensively – the old AKG CK94 (now discontinued) and the, much better sounding, new Rycote BD-10. Hopefully, something in what follows might be of interest and use to at least some others. The embedded audio clips are as recorded straight – no equalisation (unless I specify that a high-pass filter has been used: usually on the recorder), no added reverb, compression etc. – although levels have been matched in relation to mic sensitivity.

A look at the mic and its specifications
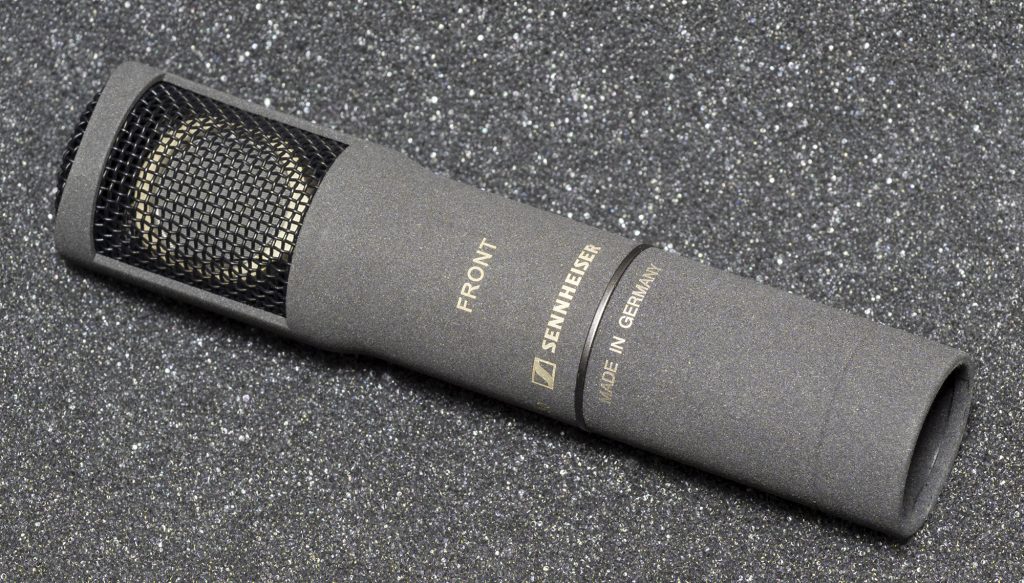
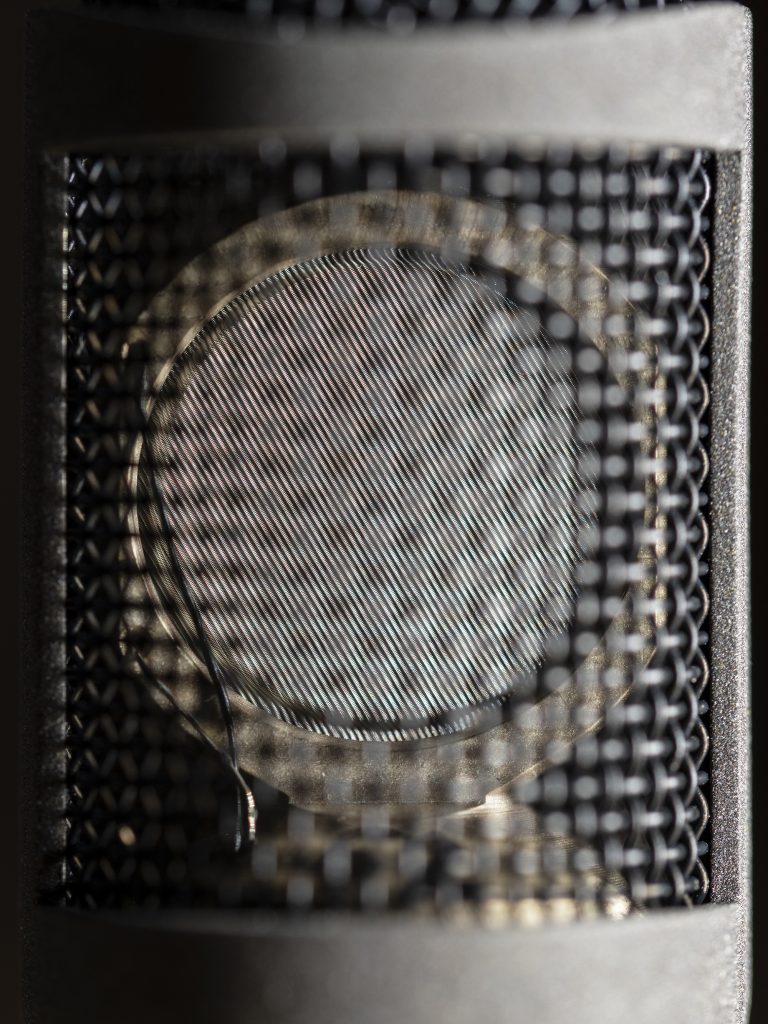
Well, first to the mic itself. The copy I have been sent by Sennheiser for field-testing is a pre-production model, although I understand that any changes before launch are likely to be limited to cosmetic matters. Peering through the fairly open weave of the basket (as on the other MKH mics) it is possible to see quite a bit of the capsule: as with the other MKH 8000 series mics it has a 16mm-diameter diaphragm (which Sennheiser has clarified in the press-release is the usual MKH symmetrical push-pull type, and evidently is a single diaphragm model), although its side-address orientation in this case means that the housing widens out from 19mm to 21mm to accommodate it. At 92mm long (with the XLR module) and weighing 71g (as measured here: Sennheiser give it as 83g in the press-release), the mic is only 33% of the size (by volume) of its MKH 30 counterpart and 65% of its weight. In short, it is small, but with some reassuring heft!
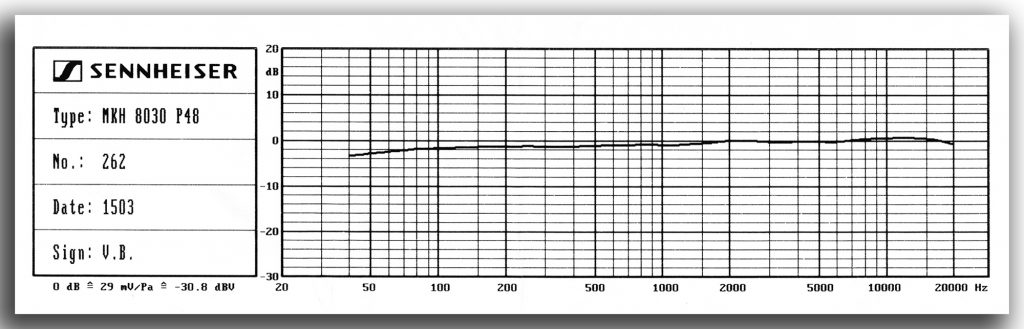
Performance-related specs published in the press-release of 15.9.2023 were limited to max SPL (139dB), frequency response (30-50,000 Hz), and self-noise (13dBA), but the individual calibration sheet supplied in the box with the sample mic usefully adds sensitivity (29 mV/Pa, -30.8dBV) and a plot of the frequency response curve (see below). These specs seem very much as anticipated. The 13dBA self-noise figure matches that for the larger MKH 30, which was expected, but is a relief all the same: most manufacturers produce fig 8 mics with self-noise significantly above their other polar patterns, but both Sennheiser’s fig 8s match their cardioid, super-cardioid and wide-cardioid counterparts in this regard. What does differ, though, is the sensitivity of the MKH 8030: this is 3dBV less than the cardioid, super-cardioid and wide-cardioid mics, close to the omni mic (1dBV more), and very different to the MKH 8060 and 8070 shotguns. This contrasts with the larger MKH 30, which, at 32dBV, matches the mics most likely to be used with it for critical MS recordings: namely, the MKH 20 omni, MKH 40 cardioid and MKH 50 super-cardioid mics. A small matter, perhaps, and certainly not relevant to all users, but it does make exact matching of gain on a mid-side linked pair a fiddle on many, if not most, recorders. Evidently more details – such as a polar plot – will follow in due course.


RFI
Looking at radio frequency interference (RFI) on the MKH 8030 is nothing to do with its RF design (which, in the words of the MKH designer Manfred Hibbing in his The MKH Story white paper), means the mic essentially has ‘a transmitter and receiver that are directly wired together’), but is about its resistance to external RFI. As I’ve said in posts on other tests, I am interested in the impact of RFI on mics since, as living in rural Norfolk, much of my life is outside or on the edge of mobile phone reception, where some models of phones transmitting at full power can cause notable interference on mics at up to, say 1m/3ft: not a problem with mics on a stand, but I’ve had this become a real issue with handheld shotgun mics and a phone in my jacket pocket (on those rare occasions when I forget to turn my phone off). And this could be a problem with ENG work too (not least from the phone of an interviewee). So I was glad to find that in testing, as before, with several different phones on the absolute fringe of reception (i.e. working at highest power) the MKH 8030 showed no sign of RFI even at close distances (100mm): for control I recorded the mic alongside a known problem mic (to check that the intermittent issue was occurring: it was) and the Sennheiser MKH 8040 (no RFI issue either). A good start!
Self-noise
The 13dB-A self-noise figure for the MKH30 and, now, the MKH 8030 mic is excellent for an SDC fig 8. The Schoeps MK8, for example, has self-noise of 17dB-A and the Schoeps CCM 8 is fractionally noisier at 18dB-A. Given that listening to the hiss of a mic on its own isn’t hugely instructive, I compared the MKH 8030 with two other 13dB-A mics that I have – the cardioid Rycote CA-08 and, more relevant to prospective users of the new mic, the cardioid Sennheiser MKH 8040 – and the 18dB-A Rycote BD-10. First off, I checked that the manufacturer’s sensitivity figures were broadly correct, recording a 1kHz tone and measuring that with a tight band-pass filter applied at 1kHz: all was evidently in order. So, l in the absence of an anechoic chamber, I then did my usual by recording the sound of nothing with the mics buried deep in duvets in the airing cupboard, with all doors and windows closed and the mains electricity turned off, recording into a Sound Devices MixPre-3 [EIN -130dBV/-128dBu]). There was a bit of low-frequency sound still permeating, so I applied a 100Hz high-pass filter at the recorder. Normally, I wouldn’t bother including the sound of madly cranked-up mic hiss (the MKH8030 has been given a whopping 70dB of gain, and the other mics even more – reflecting their different sensitivities) in a test/review, but in this case it is quite interesting, so here goes with the audio files for the two Sennheiser mics and the BD-10. Just remember, and don’t panic: all three mics are very quiet in normal use!
And here are the spectrum analyzer visualizations of the noise:
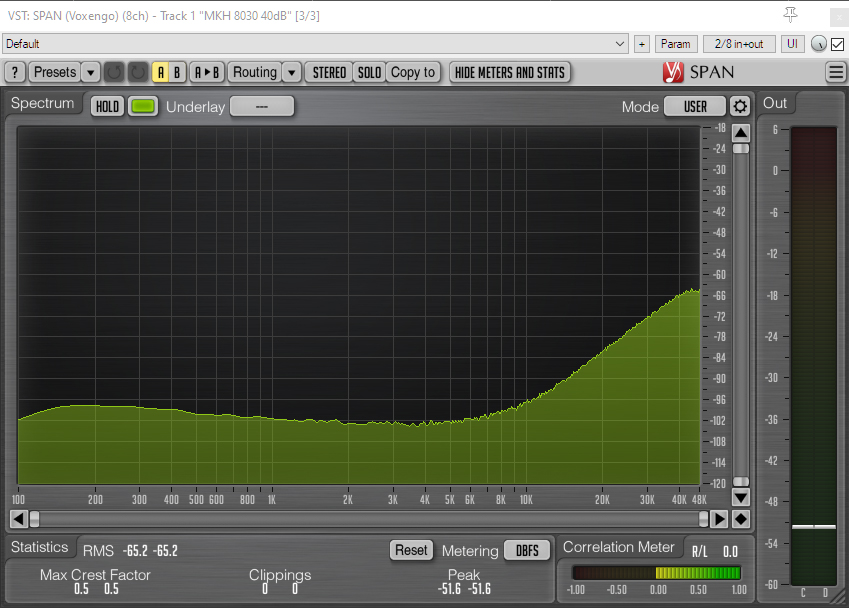
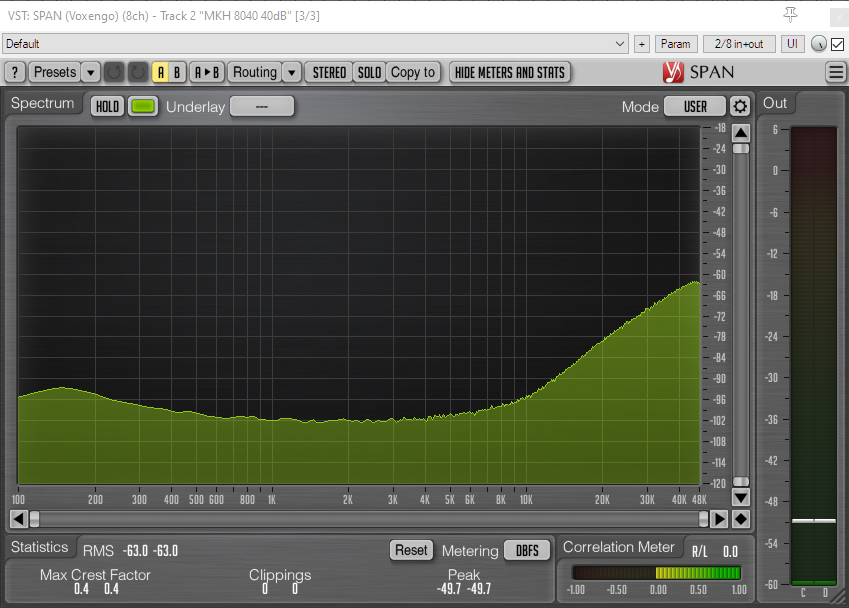
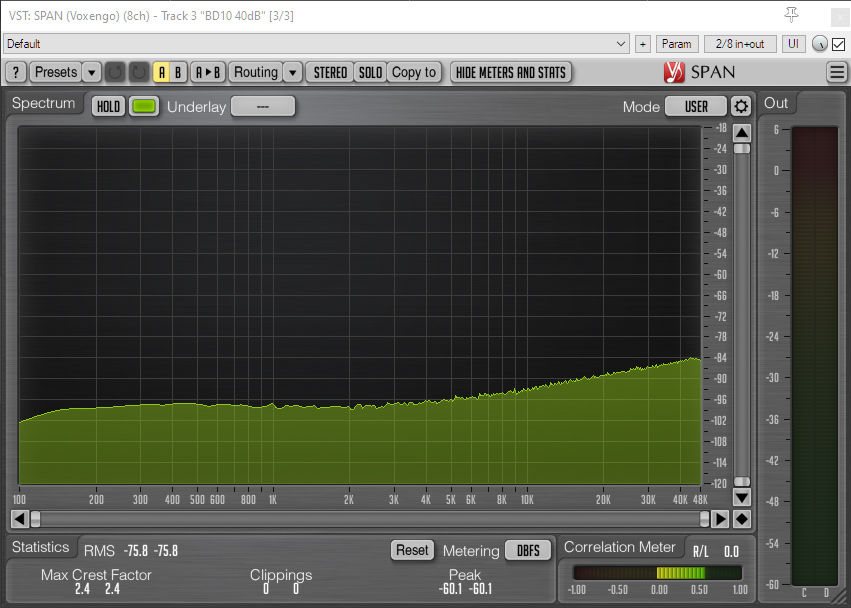
BD-10 with 79.4dB total gain (to match MKH 8030 sensitivity) and 100Hz high-pass filter
The sound files and the spectrum analyzer visualizations show that the two Sennheiser mics are broadly similar, although the MKH 8040 cardioid mic has more low-frequency noise: I suspect strongly that this is external noise resulting from my imperfect isolation, and a consequence of the different polar patterns. The spectrum analyzer also shows the increase in self-noise levels of the Sennheiser mics at very high frequencies – largely above human hearing, although relevant if pitching down (e.g. some effects, or bat recordings etc.). The BD-10 lacks such a significant rise in self-noise levels in frequencies above human hearing, but, in the realm of normal hearing has a higher-frequency hiss, which is also a little louder and more perceptible, especially if the level is reduced from these extreme gains: the greater self-noise is in accordance with the different specs [note: these tests use the revised BD-10 sensitivity of 9.8 mV/Pa/-40.2dBV, which differs by -3.25dBV from the specification published by Rycote in 2023]. Self-noise is unlikely to be the determining factor in deciding between using or buying these mics, and perhaps this also applies to the choice between the MKH 8030 and the similarly expensive 17dB-A Schoeps MK8 + CMC or the 18dB-A CCM8.
Frequency response
The press-release for the MKH 8030 gives the frequency range for the mic as 30Hz to 50kHz, and, in this regard, the fig 8 follows the rest of the MK 8000 series mics, with the upper frequency range extended compared to the earlier MKH mics and, indeed, most mics on the market. As discussed in previous posts, extended high-frequency response might seem entirely academic outside those recording at high sample rates and pitching down in post (e.g. for bat recordings, or for sound effects), but there are those that argue frequency response over 20kHz is important for high-resolution recording (such as David Blackmer of Earthworks mics in this article). Anyway, for a field test, I though the overtones of some church bells would be an interesting sample, so up I clambered to the belfry.
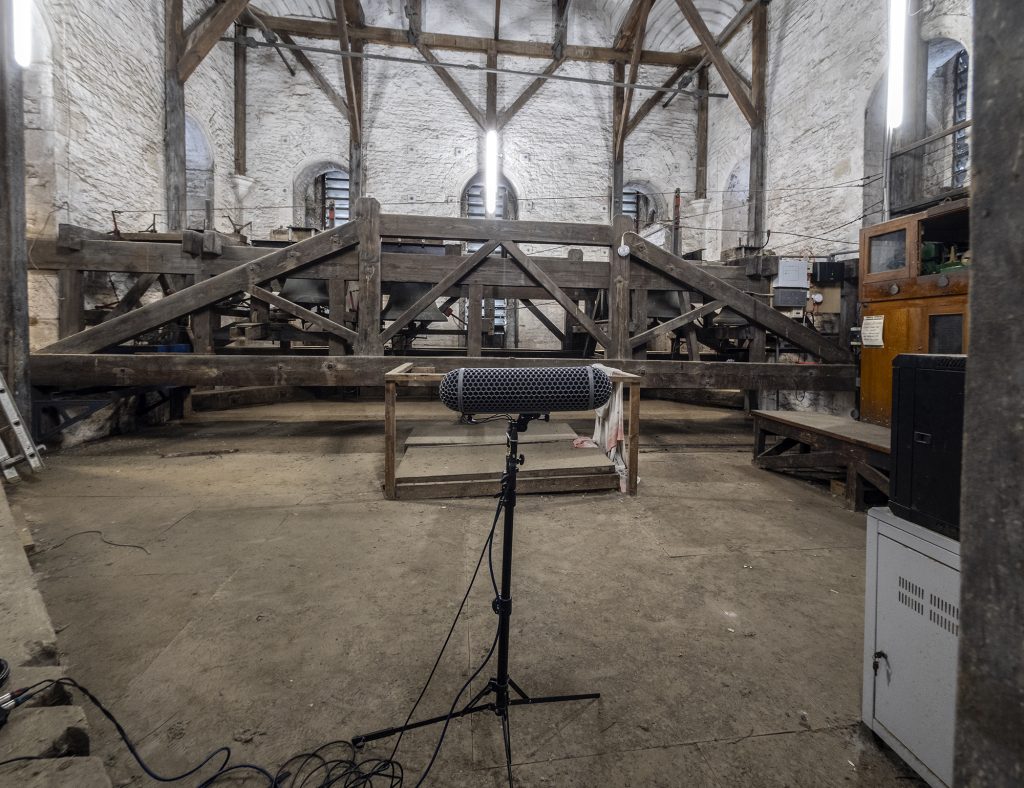

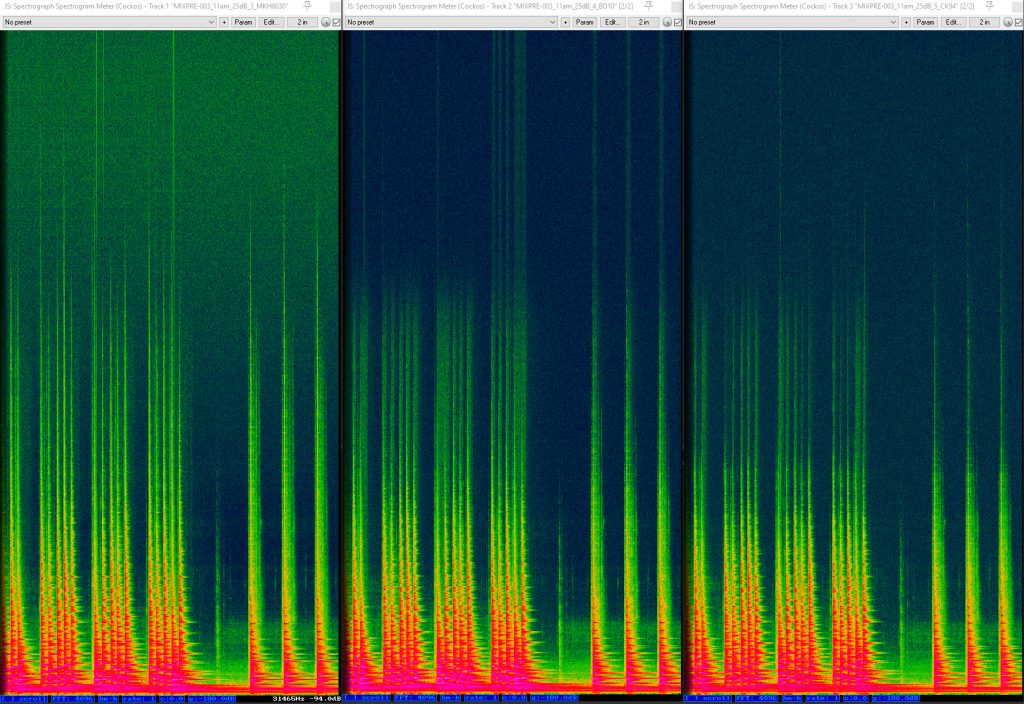
For the recording I set up three fig 8 mics (the MKH 8030, the BD-10 and AKG CK94) in a windshield (there was quite a breeze inside the belfry) facing the bell-frame. Here are the sound files.
And here is a spectrogram of part of the recording, showing the chimes. The high-frequency capability of the MKH 8030 is certainly in evidence, with much stronger signals up to 48kHz (the limit on this spectrogram), albeit with more self-noise at such frequencies. The BD-10 does reasonably well, but with lower self-noise over 20kHz, and, as expected from previous tests, the CK94 comes in third in this test.
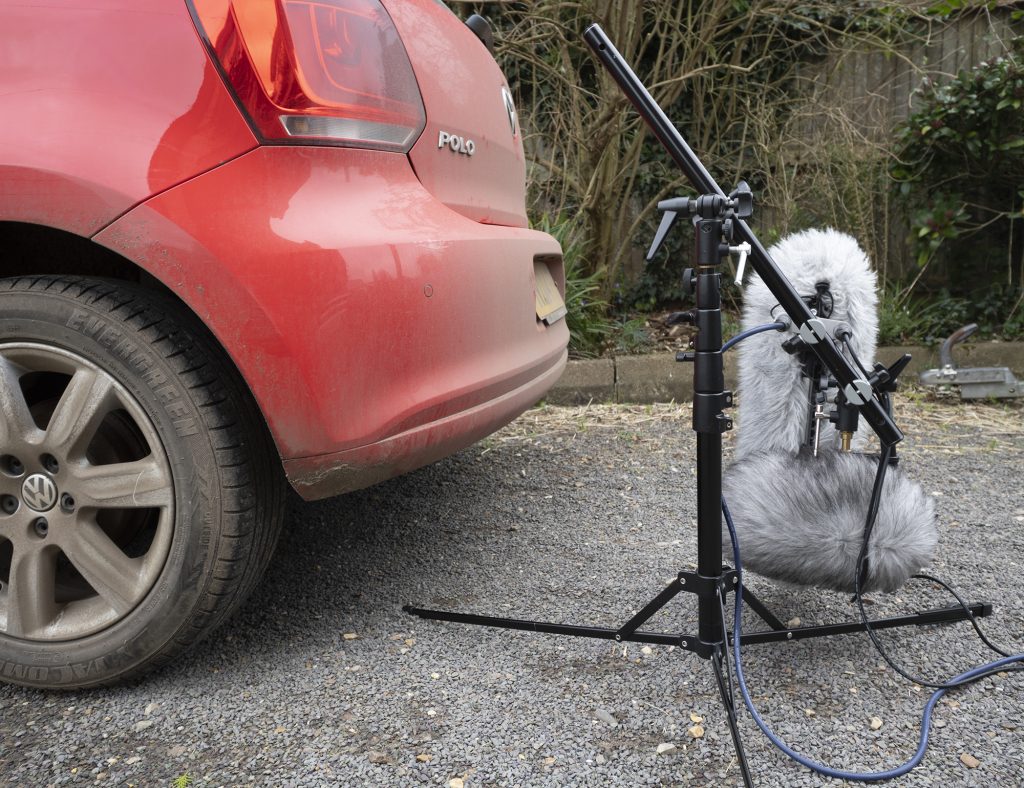

Turning to the other end of the spectrum, fig 8 mics generally have a poorer bass response than omni, wide cardioid, cardioid and super-cardioid polar patterns, although the Sennheiser MKH 30 has long demonstrated that it is unusually capable at lower frequencies. The MKH 8030 specs promise similar performance. In this case I took three fig 8 mics (the MKH 8030, Rycote BD-10 and AKG CK94) and oriented them so that in each case one of their lobes faced the exhaust pipe at the rear of a parked car and, in a separate blimp immediately adjacent, set up the cardioid MKH 8040 likewise facing the car, which was then started and left idling.
And here are the spectrum analyzer visualizations:
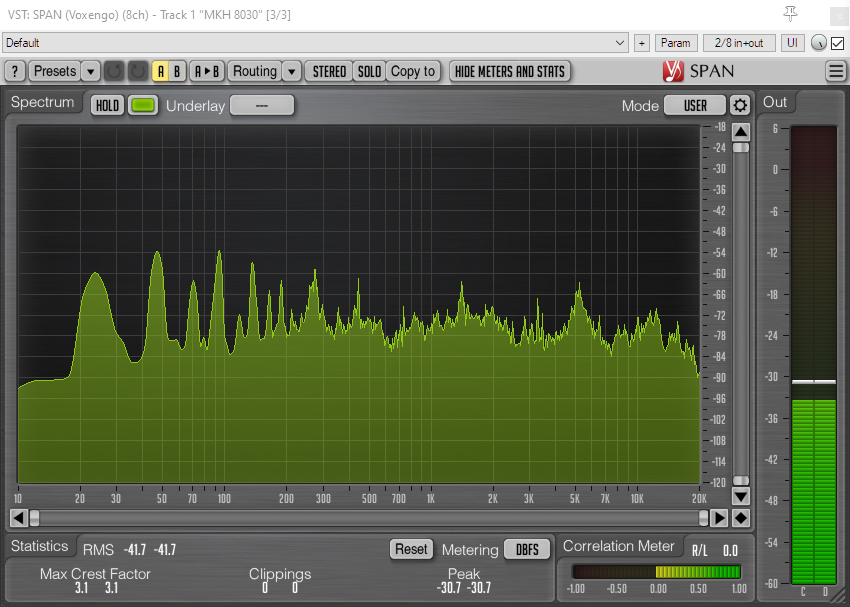
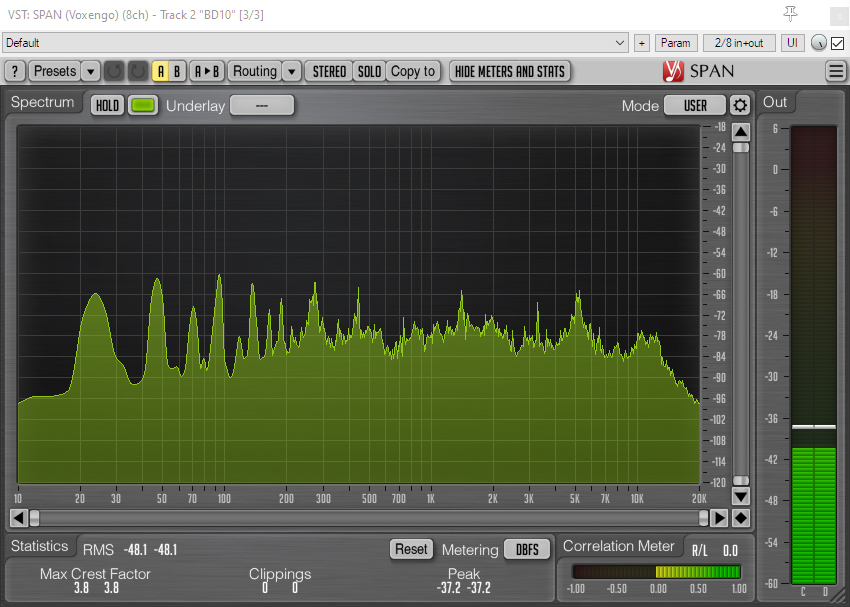
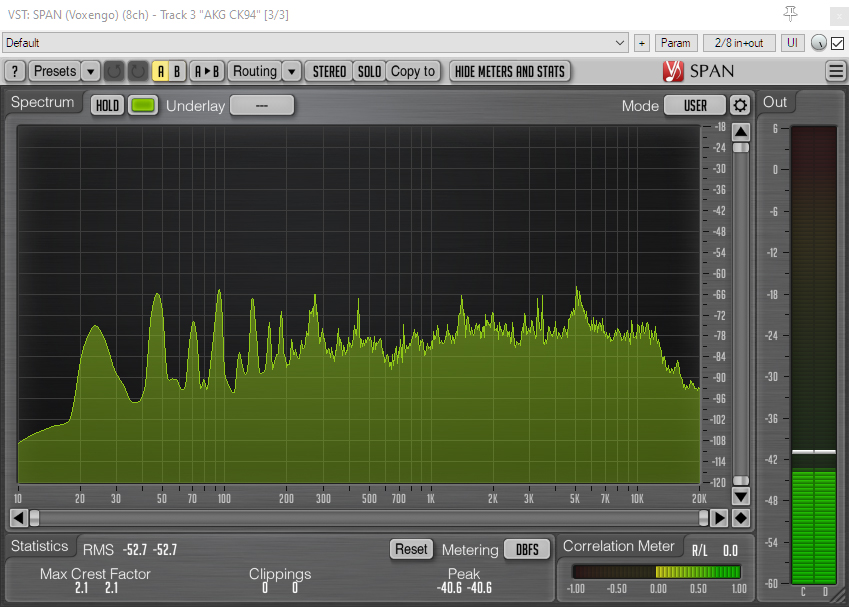
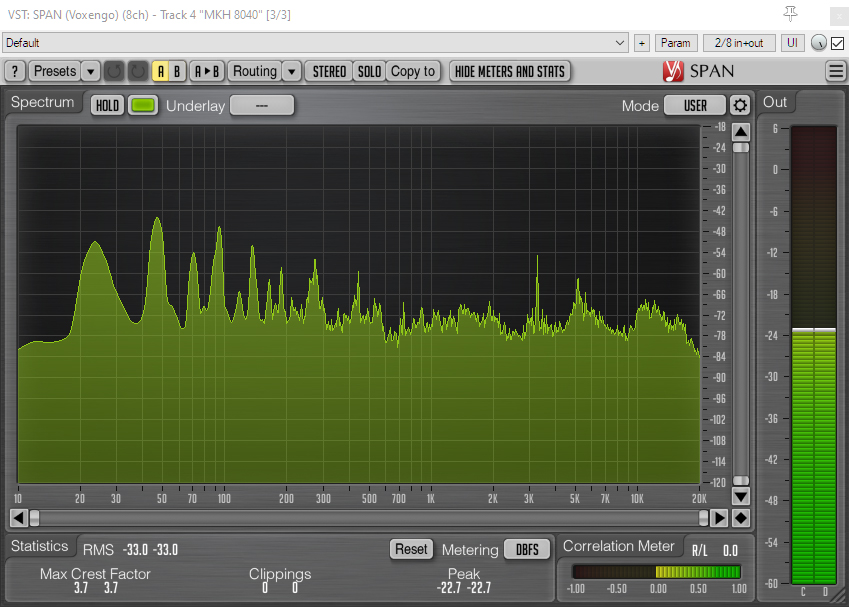
The tracks show all four mics capable of rendering the lowest fundamental, with the MKH 8030 showing a better low-frequency response than the Rycote BD-10, and the latter showing a much better low-frequency response than the AKG CK94. At the lowest fundamental of around 22.5Hz the MKH 8030 was about 6dB louder than the BD-10, and the BD-10 about 9dB louder than the AKG CK94. The MKH 8040 has an unusually good bass response for a cardioid, and the peak at 22.5Hz was 9dB louder than that with the MKH 8030: in truth the low-frequency content of the cardioid mic is a little overwhelming in this test. Such a low frequency as 22.5Hz is beyond the quoted specs of the MKH 8030, and sticking mics by a car exhaust is hardly the most scientific test, but the general point is well illustrated by the audio files and the peaks in the spectrum analyzer visualizations: that is, the MKH 8030 has a good low-frequency response, but, as I have found previously when testing fig 8s, in the field at least this falls short of a decent cardioid or, obviously, an omni mic. This fuller low end of the MKH 8030 compared to the other SDC fig 8 mics I have to hand is evident through any of the recordings I made during these tests that have lower frequency content. It will be for others to see how this compares to the MKH 30, the Schoeps fig 8 etc., or even whether such very low-frequency response matters in a fig 8.
The nulls
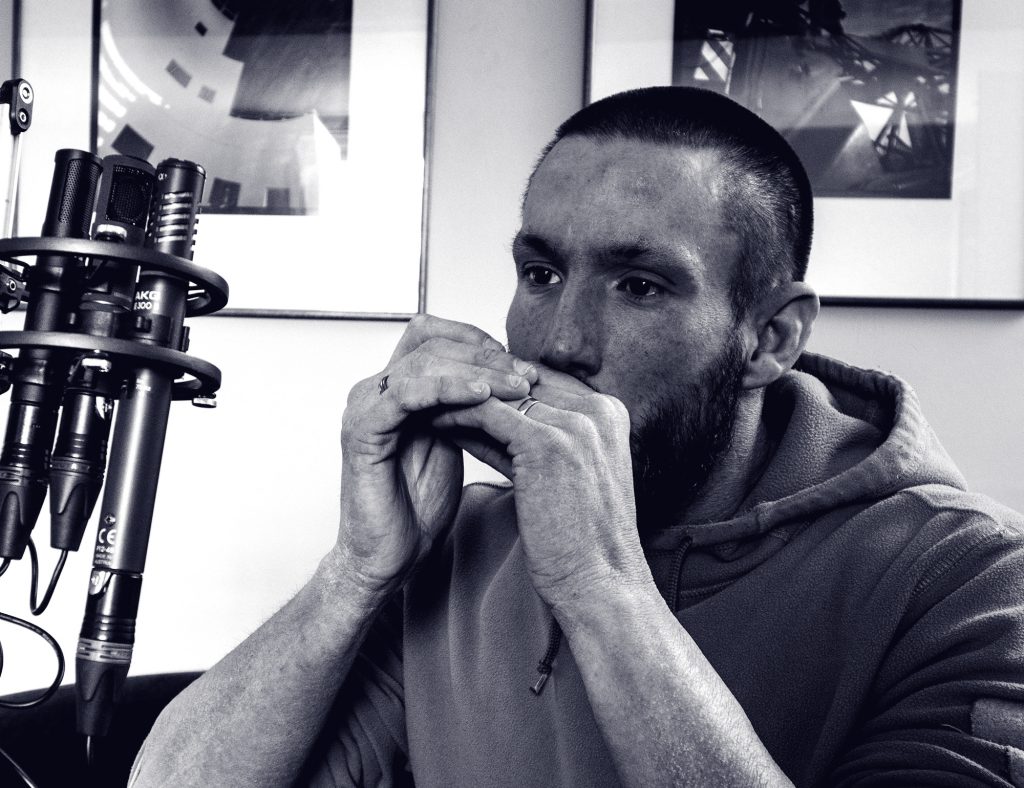

At this stage there is no available polar plot for the MKH 8030, but – from the MKH 30 – expectation is high that the new mic offers similarly deep nulls, which are an essential characteristic of a fig 8 mic. It is hard to test this accurately in the field, as opposed to in an anechoic chamber, so what you have here is a bit of a rough and ready test: some blues harp playing courtesy of Andy Chinn at about 400mm from the MKH 8030, along with the BD-10 and CK94 fig 8s. This snippet is then followed by a brief silence, after which is another recording with the mics rotated 90 degrees: Andy’s playing and position remain unchanged.
Not hugely conclusive, I know, not least given that the sound was reflecting around the modest-sized living room – so not doing the nulls justice (although something of a real-world reality check) – but, nonetheless, there was a measurable difference in the effectiveness of the nulls: the MKH 8030 produced a 12.5dB drop in LUFs; the BD10 an 11.2dB drop in LUFs; and the CK94 a 10.7dB drop in LUFs. Of course, the on-axis and null recordings were not simultaneous (or identical) so these figures are only indicative, and I strongly suspect that the differences will be more substantial – certainly against the CK94, which doesn’t have the deepest of nulls (but is still effective in this regard) – in a larger space or, of course, outdoors. Anyway, nicer to listen to a bit of blues harp than a car exhaust!
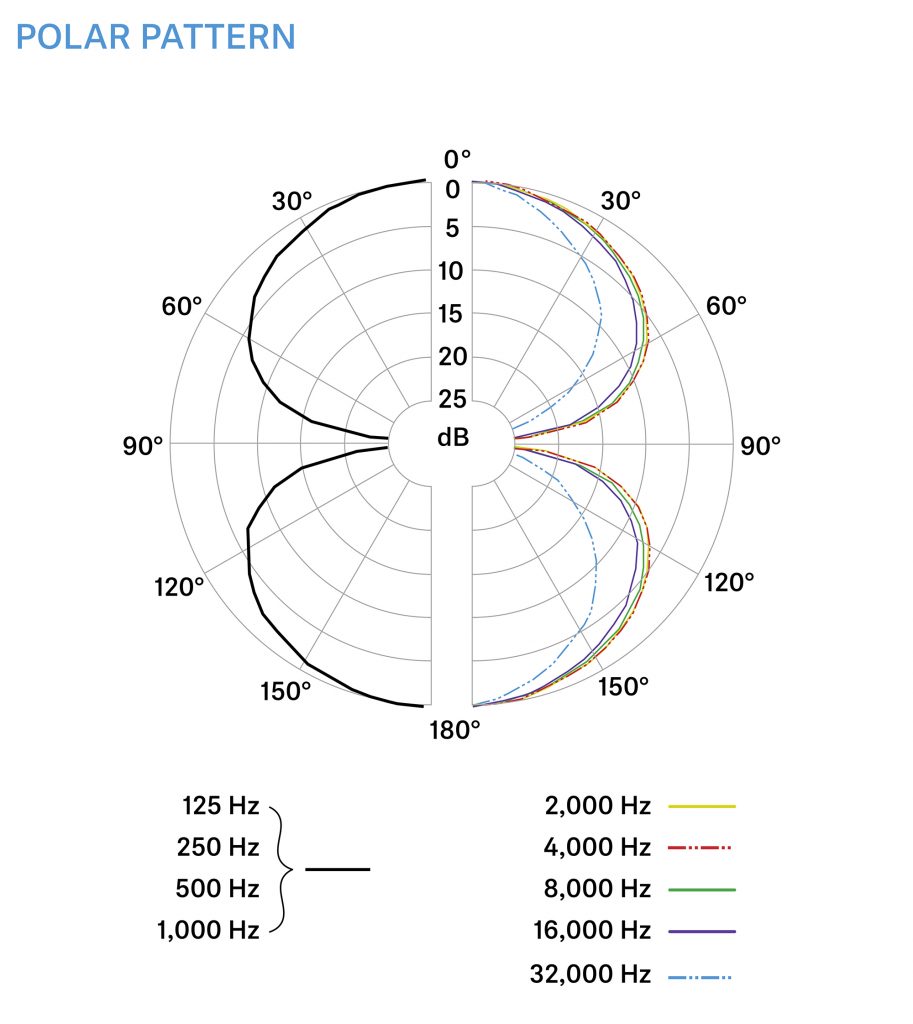
EDIT (9.4.2024): Sennheiser have now produced a specs sheet (in advance of publication at NAB 2024), which includes the following polar pattern and confirms that the MKH 8030 measures similarly to the MKH 30 – excellent news:
Handling noise
The MKH 8030 is likely to become a regular fixture in windshields on boom poles or on a pistol grip, such as for those times when a bit of ambience is required during production sound recording, or perhaps to get closer to a difficult to access source during field recording. In short, while it may not be swinging around as fast as in some cases of mics used for booming for dialogue,the MKH 8030 is likely to be handheld at times and also to be used on a boom pole. So, with that in mind, I put the mic through some boom-pole handling tests.
All other things being equal, fig 8 mics are the most susceptible to handling noise. Three mics were included in the test (i.e. rigged in Rycote Invision suspensions on a short stereo bar on the end of the boom pole) to allow comparison: the MKH 8030, the MKH 8040 and the Rycote BD-10. Gain levels were adjusted for relative sensitivities.
When holding the boom pole statically (extended and horizontally) all three mics showed some handling noise, with the MKH 8040 being the most significant, peaking at -26.1dB, with LUFs at -55.8dB; the MKH 8030 was significantly better, peaking at -32.2dB, with LUFs at -61.3dB; and the Rycote BD-10 was better still, peaking at -35.5dB with LUFs at -67.0dB. Evidently this was trembling/vibration from the boom operator’s muscles holding a steady stance, and was all low-frequency energy below c.50Hz: a high-pass filter of 80Hz – a pretty essential adjunct to booming – removes such energy. In the second series of sound files, the mics were held as previously, but the boom pole was tapped with at the grip point to test transmission of louder handling noise. As expected, the results are similar to the static hold test, with the cardioid MKH 8040 performing least well (-51.2 LUFs), followed by the MKH 8030 (-56.4 LUFs) and then the BD-10 (-57.9 LUFs). Doubtless the extended low-frequency capability of the cardioid MKH 8040 is the reason why it is outperformed in this handling test by the two fig 8 mics. The MKH 8030 should offer no problem to the user given, in addition to use of a high-pass filter, a suitable suspension and experienced boom operation (not forgetting that capture of stereo ambiences on a boom pole is usually for incidental B-roll, camera perspective stereo etc., not whilst executing complex and rapid boom pole movements for dialogue recording!).
Wind noise
Fig 8 mics are especially susceptible to wind noise, so it is interesting to explore this aspect of the MKH 8030’s performance. To get a base line, a triple rig of MKH 8030, MKH 8040 and BD-10 was used, again with the mics in separate Invision suspensions, spaced along a stereo bar so that no mic was shielded from the wind by the others, and mounted on a boom pole. Fast boom swings were made to generate wind noise in a controlled fashion, not to represent typical usage of a fig 8. Gain was set as for the handling noise tests (see above). Swinging the bare mics produced overwhelming rumble, as would be expected: the MKH 8040 cardioid was easily the most sensitive in this regard, which again goes against what one might expect with a cardioid vs a fig 8. Of course, such use is unrealistic: even with a modest amount of boom movement indoors (or the gentlest air movement around a static mic indoors) at the very least a foam windshield would be used, so the test was repeated with the manufacturer’s original foams on all three mics (NB the foam for the MKH 8030 is specifically made for the mic, and is much wider than that for the MKH 8040, reflecting the different orientation of the capsule). The boom was swung in vertical and horizontal arcs, with very little difference in the results: the sound files below are for horizontal arcs, which, usefully, could be rather longer. In this case an 80Hz high-pass filter was set on the Sound Devices MixPre-3 recorder.
Again, and very much as expected given the boom handling experience, the cardioid MKH 8040 fared less well, with peak levels at -20.9dB and -38.2dB LUFs; while the two fig 8s performed very similarly – the MKH 8030 giving a peak of -27.2dB and LUFs of -44.5dB, and the BD-10 a peak of -27.1dB and LUFs of -45.4dB. I have been using the BD-10 in the field for some time now and it is reassuring that the MKH 8030 is very closely matched in terms of performance (at least once an 80Hz high-pass filter is applied: the ambient mid-side test, below, reveals a little bit more wind susceptibility when no filter is applied, as would be expected given the fuller lower end).
Now back to some more musical tests…
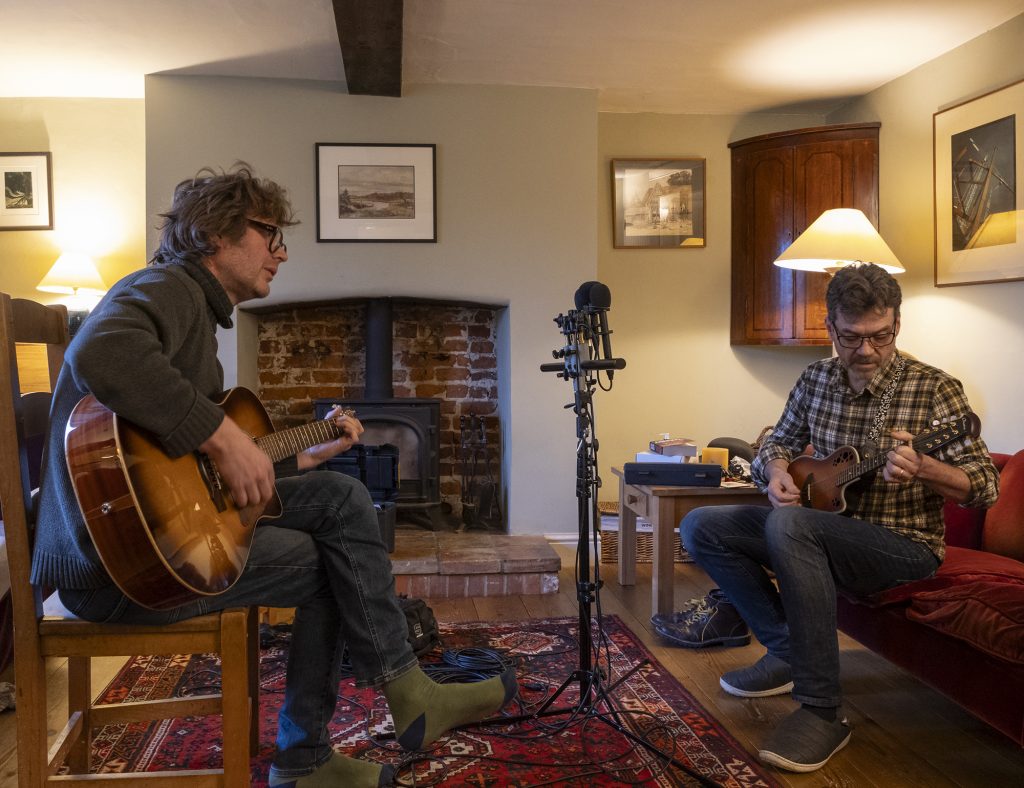

While it is useful to explore some aspects of the performance of the MKH 8030 in isolation, of course it is vital to get a sense of how the mic actually sounds: deep nulls, low self-noise etc. don’t necessarily mean you want to use the mic!
In this test, the two musicians first chat about how to play the song , so this provides a useful voice test on-axis to the mic: they are sitting one in front and one behind the mics, so on axis to the two lobes of the mic. Then the two start to play: Jo on mandolin and vocals, Richard on a bit of gentle guitar backing to what is an unfamiliar song to him. Maybe not the ideal way to mic two instruments and a vocal, and certainly not the ideal room, but it is a not a serious studio recording and gives a flavour of the mics.
This is pair of tests certainly shows up the difference between the two mics. How much that is the different frequency response, how much is increased detail resulting from a push-pull symmetrical capsule etc. – well, I’ll let you decide!
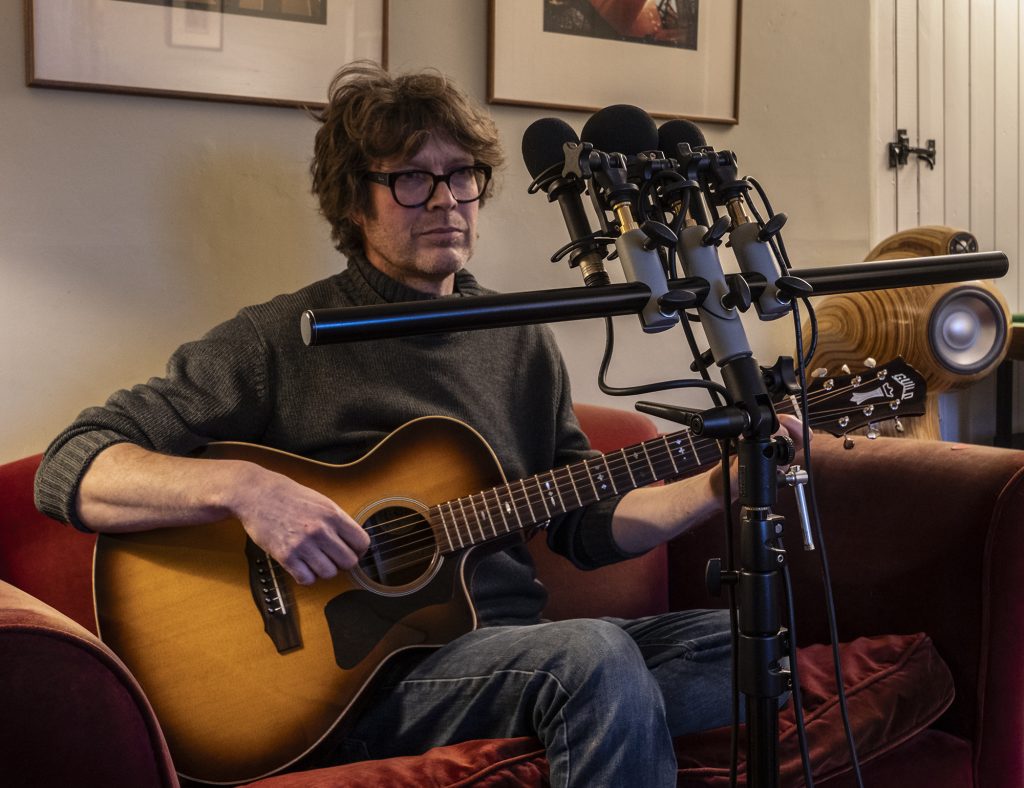

Focusing now on a bit of steel-strung acoustic guitar by Richard, the mics were moved a little closer, so with a bit of proximity effect coming to play, here are the sound files for the recordings with the MKH 8030, Rycote BD-10 and AKG CK94:
How does the MKH 8030 sound compared to the other MKH 8000 series mics?
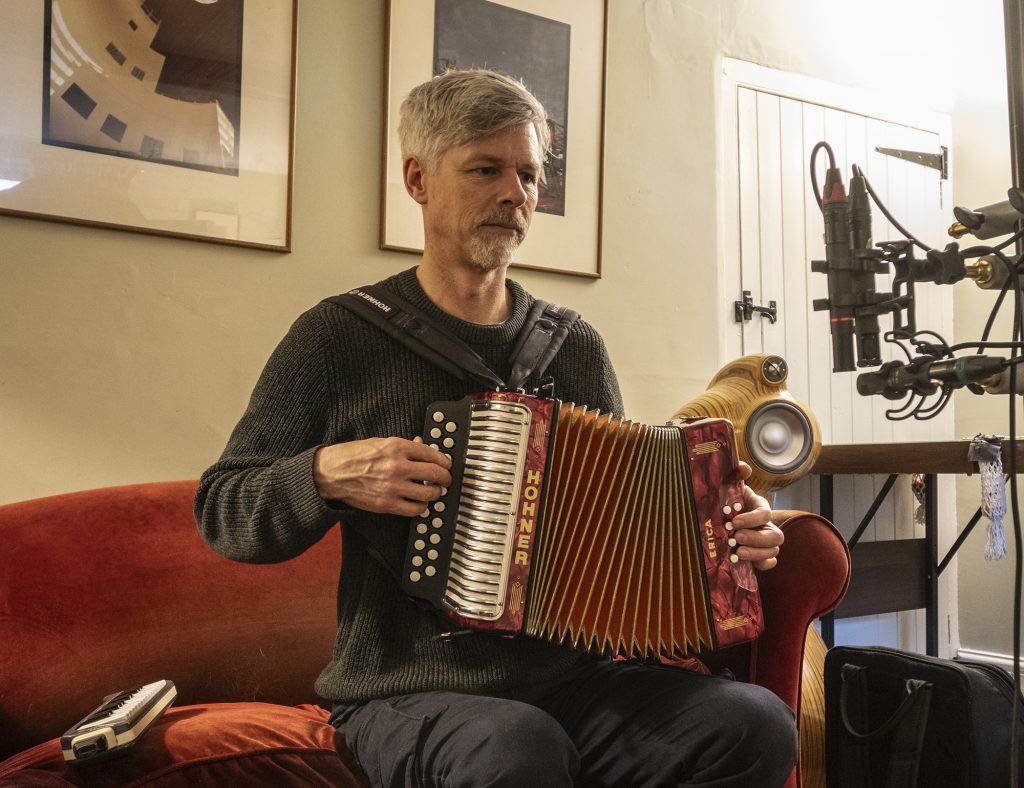

Comparing the sound of mics with different polar patterns is not easy, and the fig 8 offers particular challenges in that regard, what with its front and back lobes. But I had a stab, setting up the fig 8 with an MKH 8040 cardioid mic, so both were aimed directly at the musician. To reduce the impact of the rear lobe of the fig 8, I placed a pair of tall gobos about 800mm behind the mics. As you can see from the photo, I also included a Rycote BD-10 in the recording, so here are three files for a bit of melodeon (from Drink Up The Cider):
The different low-frequency responses of the mics is evident: the MKH 8040 is a little fuller than the MKH 8030, but they are fairly consistent; the BD-10’s lighter low end means it sounds rather different.
Turning then to something with less low end, I then recorded Rob playing a bit of melodica (a bit of Raggletaggle Gypsy):
As would be expected, the differences between the three mics are more subtle and, at least, are not just limited to the fuller low end of the MKH 8030.
And, finally, a bit of unaccompanied singing (a snippet of North Sea Holes), as before, but with a pop filter placed in front of the mics:
Again, the frequency range of the singing (mainly above 150Hz) means that the difference between the mics is not as exaggerated as with a bass-heavy source, and the two Sennheiser mics sound pretty well matched, with the BD-10 a little less full.
And what about mid-side?
There is no denying that one of the key uses of the MKH 8030 will be as the side mic in a mid-side or even a double mid-side set-up. Obviously a mic of any pattern can be used as the mid mic: when used for production sound, to give a stereo option on set, the mid mic is likely to be a super-cardioid or, even, a shotgun mic; for some effects recording a super-cardioid may again be a good option; but by far the most regular mid mic in MS is the cardioid mic. With equal gain (or with the gain tweaked to compensate for different mid and side mic sensitivities) the mid and side mics in the latter case give, when decoded to LR stereo, a stereo recording angle that matches a pair of cardioid mics used as a 90-degree XY pair, although the mid-side recording often sounds rather different with the mid-mic typically being on axis to the main sound source.

I kicked off mid-side tests on vocals with a bit of unaccompanied music hall – What a Mouth (What a North and South) – recorded with the MKH 8030 as the side mic and a Rycote CA-08 as the mid mic : for comparison I recorded this in parallel with a Rycote BD-10 and Rycote CA-08 MS pair. Obviously, the same mid mic takes the main source – Matt’s voice direct to the mic – so that the difference in the side mics is subtle: some ears may hear the difference.
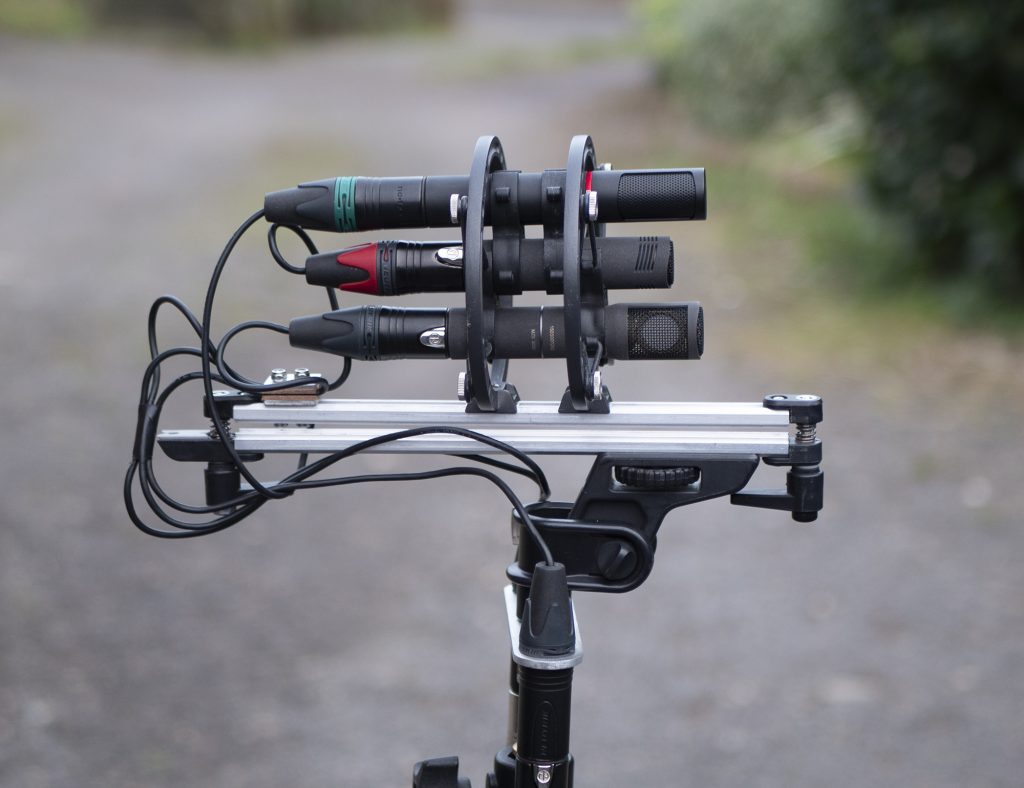

At the opposite end of the spectrum, I took the an MS rig outside for some ambience recording, where the sounds came from all around. For this, I did one of my regular test recordings in this nominally quiet Norfolk village, with birds a-singing, a pheasant squawking, the odd shotgun going off (perhaps the pheasant had good reason to squawk), cars driving past etc. In this instance I set up a triple mic array as in the photo above, with a cardioid MKH 8040 centrally, with fig 8 mics above and below – that is, the MKH8030 and the Rycote BD10.
The differences are subtle, but discernible. Most noticeable is the increased bass response of the MKH 8030 vs the Rycote fig 8, which doesn’t always work in the mic’s favour: the effect of the fairly fresh wind is more noticeable on the MKH 8030 MS recording, despite the use of a full blimp and fur (admittedly, with the two fig 8s fairly near the edge of the basket – so hardly ideal). And the greater bass response of the fig 8 mic increases the side mic output, so makes for what might be perceived as a very slightly wider stereo image, but is, in reality, a more consistent stereo image into lower frequencies (say 150Hz-200Hz and lower).
Conclusions
Well I’m a fan of fig 8 mics, using them routinely for their deep nulls (e.g. when recording singer-guitarists, and wanting some separate control over vocals and instrument) and, especially, for mid-side recording. And recently I have begun to enjoy the delights of Blumlein pairs. I had high hopes for the MKH 8030 and it hasn’t disappointed: so impressed have I been that during the time I have spent with the mic, I splashed out and bought a new cardioid MKH 8040 so that I could use the MKH 8030 with one of its siblings (rather than mics from other manufacturers) for these tests and for future mid-side recording .
The MKH 8030’s match with the MKH 8040 is excellent, so it is hard to think that it will disappoint anybody used to the MKH 30, although, course, some will prefer to use the larger mic, just has been the case with the MKH 40 vs MKH 8040 etc. previously: at the top end, engineers pick mics on subtle distinctions that they – with their different preferences – feel best suit the source and the application, and this will include other makes of SDC fig 8, such as Schoeps’s options. Looking further down the scale, the MKH 8030 is a massive jump from the mid-priced (and now discontinued) AKG CK94, and has a discernible edge over the Rycote BD-10. This does such more budget-friendly mics no disservice at all: at over twice the price of the BD-10, for example, the MKH 8030 should be expected to outperform it. If you are in the market for a fig 8 SDC mic and have a budget in the region of £1500, then there is no doubt that you should give the MKH 8030 careful consideration (and a listen): in addition to its sonic and size attributes, in common with all the MKH RF mics the MKH 8030 promises very high resistance to humidity, which may be a key feature for some recordists. If such prices are out of reach, then the Rycote BD-10 presents an excellent proposition, and, for alternatives, it might well be worth exploring whether MBHO still produce the KA 800 fig 8 capsule (the MBHO website has long since failed to list the capsule), whether the Ambient Emesser ATE 308 meets your needs (e.g. if combining with a shotgun mic), and whether other options, such as B9 Audio’s CM180, might be of interest. Fig 8 SDC mics don’t grow on trees, but there are options out there from around £600 upwards. Below that, dual diaphragm LDC multi-pattern mics may well provide what you need: indeed, a high-end LDC multi-pattern mic might be what you prefer when wanting a fig 8 for a particular application. The MKH 8030 is at or very near the top end of SDC fig 8 mics, but the important thing is to have one or two, three or more fig 8s in your mic locker!
NB Stayed tuned if interested so far: on Thursday I’m due to be recording a bluegrass band – The Time and Mercy Band – in a studio, ranged round the MKH 8030 and MKH 8040 MS pair, and I’ll include the Rycote BD-10 and CA-08 cardioid too, to allow a range of MS combinations. There will be a write up, with sound files and video too: this post is already long enough, so I thought a follow-up would make more sense.




21 Comments
What a timely and very thorough review! Thank you.
Thanks Malte!
Great review
I am looking forward so much listening and using this mic
Thanks Martijn!
I think I would like the MKH8030 to go with my 5 other MKH8020s. Good review. Jake Base2 Music
Thanks Jake!
[…] Thursday evening was an inauspicious time to be heading out for a recording of a bluegrass band: it was a soggy wet evening here in rural Norfolk, with the narrow roads full of potholes lurking below rivers. It didn’t feel much like the Appalachian Mountains. Was it left, right, left, right, left and right again on the maze of roads around Mannington and Wolterton, or the other way round? And if I didn’t remember my left from my right, how on earth would I remember how to connect up the mics for some more mid-side recordings, building on my earlier comparative tests of the new Sennheiser MKH 8030? […]
They finally released this bloody thing. Bit late Sennheiser, I have a family now. 2018 would have been better. The consequences of dropping $3000 on microphones this year and disappearing for day to record trains would be fascinating but I do not wish to personally experience them.
Great testing and write up Roland, and great blog in general. Refreshing corner of the internet, Looking forward to trawling it👍
Thanks for the kind words Ben: much appreciated!
Cheers,
Roland
Incredibly thoughtful and engaging review, Roland. Thank you. A bit of a tangent, but in your experience how weather-proof are the Rycote’s in comparison to the MKH’s? For example, using the Rycote’s for field recording drop rigs like I do with my MKH 8020’s in very damp environments.
Thanks Sal. I can’t pretend that I have left MKH or Rycote mics outside as drop rigs in any conditions, let alone very wet. I’ve not had any problems with the Rycotes over a few years in damp English weather, but that’s hardly an extreme test: I’d expect electrets like them to be pretty good, and certainly George Vlad – in his reports of using the Rycotes along with MKH mics in more severe conditions – has not had issues. Sorry not to be more definitive!
Cheers,
Roland
Appreciate your honesty, Roland. English weather can be pretty moist I’d say. I always enjoying hearing about George Vlad’s exploits. Were these reports he provided personal exchanges or did he document them online? Would love to learn more.
Hi Sal. The George Vlad reports on his experiences with the Rycotes are online: I think on the Field Recording FB group. You could always contact him direct for more. I’ve sometimes thought about humidity tests for various mics, but, having never had an issue with such conditions – England may be damp (especially at present!), but it isn’t tropical – it’s neither been a pressing issue nor one I have experience with. Cheers, Roland.
Thanks Roland, I’ll check out that group. Looking forward to hearing more from you.
Do you think you’d need the MZF 8000 II for infrasound ?
I can’t say that the need for an MZF 8000 II filter module for the MKH 8030 is immediately obvious: as I show in the review, the very low bass end of the mic (while good for a fig 8) falls well short of, say, the MKH 8040 (and, of course, the MKH 8020 has much more low end still). But whether the MZF 8000 II would be of use/needed to stop the mixer/recorder preamps being overloaded by infrasound (or just to mean that files with infrasound aren’t being handed on to post) will, of course, depend on use: for example, if using as part of an MS pair on a boom (and I’m guessing – possibly erroneously! – that’s your concern), how much infrasound handling noise will there be when recording stereo (as opposed to more vigorous boom movements for recording dialogue with a shotgun/supercardioid mic alone)? So, in short, a hard one to answer!
Cheers,
Roland
Certainly the MKH8020 will go down to around 10 hz. Usually a omni mic is made with a tiny hole to prevent it acting barometrically. But one mic that is practically a barometer is the Earthworks series of mics. One quickly sees the uselessness of such low frequency ability – huge transients are recording just opening doors! So in my case, where I record organs, I am only interested in 16 hz and above, so a mic that can do 10 is good enough, and often, to silence things that would otherwise be un-noticed, like truck exhausts and fans, I usually roll off at 14 hz to remove those ‘sounds’, as all they do is make the speaker cones flap about needlessly, and in some cases dangerously.
[…] and very much not laboratory conditions for comparing self-noise. As for the self-noise tests in part 1 of the MKH 8030 tests, I used a 100Hz high-pass filter since it was impossible to keep out the very low […]
[…] series of field tests of the new Sennheiser MKH 8030 fig 8 (which kicked off with initial tests, moved on to mid-side recording, encompassed field recording, included comparison with the MKH 30, […]
[…] this case the excellent new Sennheiser MKH 8030, which I have been testing in various blog posts: see here for part 1), combined with a supercardioid for the vocals (I went with a Sennheiser MKH 8050). To keep it […]
[…] Of course, not all single-diaphragm fig 8s have such deep nulls as the MKH 8030, with, for example, previous tests showing the AKG CK94 having about 1.8dB less attenuation in the null. There is also a suggestion […]